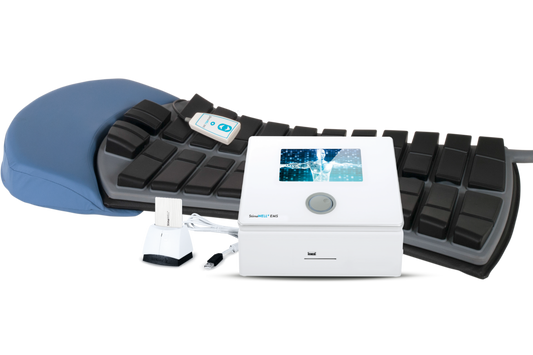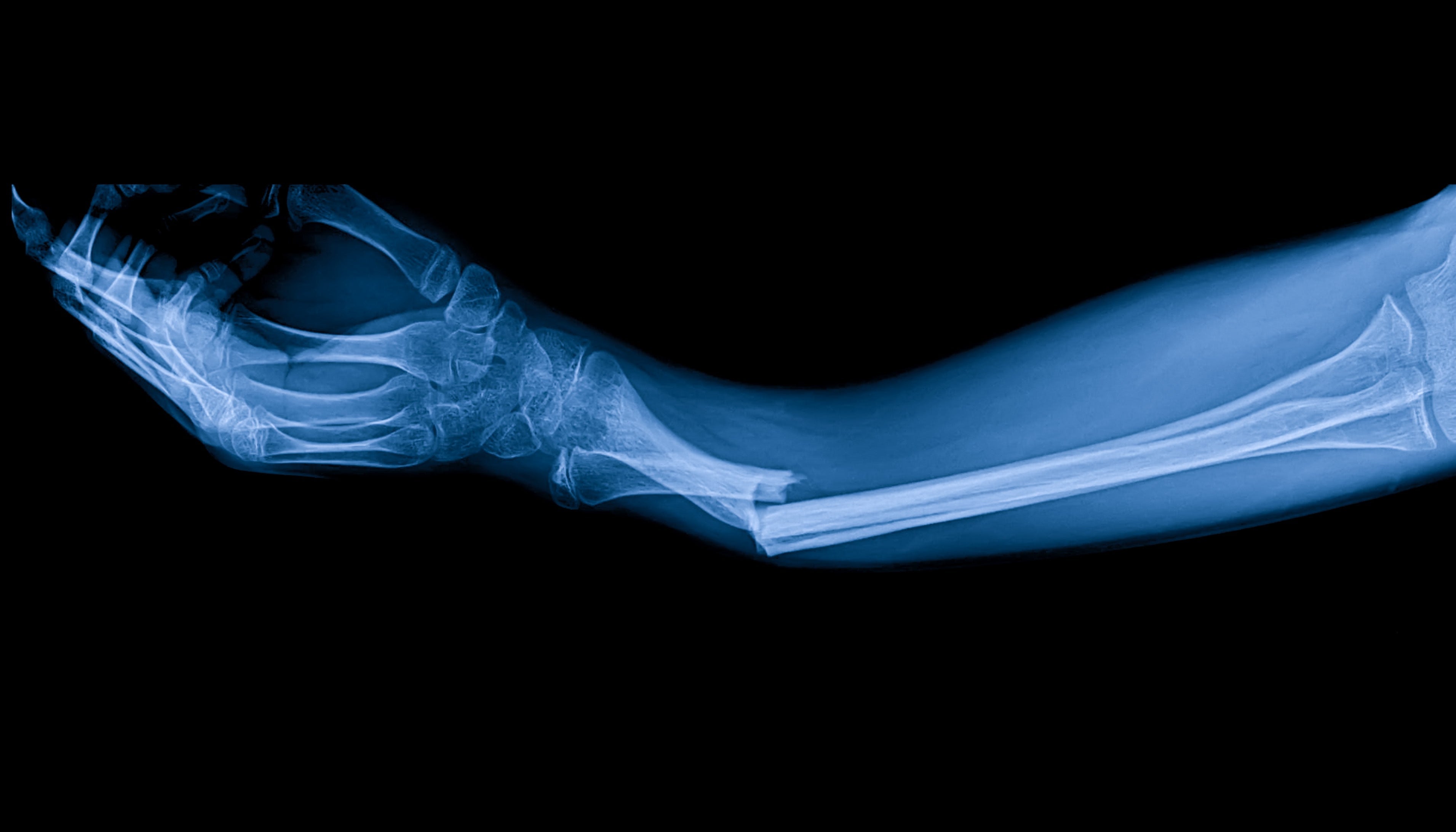
PEMF THERAPY FOR BONE FRACTURES
PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy is a revolutionary, non-invasive technology used to accelerate the healing of bone fractures. By leveraging the benefits of electromagnetic fields, a PEMF mat can significantly enhance the body's natural healing processes, making it an invaluable tool for anyone recovering from a bone fracture. Here’s a detailed exploration of how PEMF therapy aids in bone healing and why investing in a PEMF mat could be critical for a faster, more effective recovery.
Understanding Bone Fractures and PEMF Therapy
Bone fractures can result from accidents, falls, or sports injuries, requiring a significant recovery period that varies depending on the severity and location of the fracture. Traditional bone healing methods include immobilization with casts or splints, and sometimes surgical interventions. PEMF therapy complements these methods by stimulating cellular repair and bone growth at the molecular level.
How PEMF Therapy Assists in Healing Bone Fractures
Acceleration of Bone Growth and Repair:
PEMF therapy has been shown to stimulate osteoblasts—the cells responsible for bone formation. The electromagnetic fields enhance the production of proteins essential for bone growth, effectively speeding up the bone healing process.
Reduction of Inflammation and Pain:
Inflammation is a typical response following a fracture, often leading to significant pain. PEMF therapy helps reduce inflammation and pain by modulating cellular activities involved in the inflammatory process. This not only makes the recovery more comfortable but can also accelerate healing by reducing swelling that might otherwise impede the supply of nutrients to the fracture site.
Enhancement of Circulation:
Improved blood flow is crucial for delivering nutrients and removing waste products from the injury site. PEMF therapy enhances microcirculation, which supports the healing process by ensuring that essential cells and nutrients are efficiently delivered to the fracture site.
Stimulation of Cellular Energy:
PEMF therapy increases cellular energy levels (ATP) which boosts the cells' ability to repair themselves. Higher energy levels in cells at the fracture site mean faster and more efficient healing.
BENEFITS OF USING A PEMF MAT
Our PEMF mat is designed to maximize the therapeutic effects for individuals recovering from bone fractures:
Comprehensive Treatment Coverage:
The large surface area of the mat allows for a broad treatment range, ensuring that it can be effectively used for fractures in various body parts, including limbs, ribs, and vertebrae.
Customizable Settings:
Bone healing can vary by fracture type and individual healing rates. Our mat offers adjustable settings for intensity and frequency, allowing users to tailor their treatments to their specific needs, thereby optimizing the healing process.
Ease of Use:
Designed for convenience, our PEMF mat can be used in the comfort of your own home, enabling daily treatment without the need for frequent visits to medical facilities—ideal for patients in recovery who may have mobility issues.
Safety and Comfort:
Built with high-quality materials, our mat is safe and comfortable for regular use, ensuring a positive experience during each therapy session.
CONCLUSION
Incorporating a PEMF mat into your recovery strategy for bone fractures offers a unique and powerful tool to enhance and expedite healing. By improving cellular functions, reducing pain and inflammation, and stimulating bone repair, PEMF therapy can significantly shorten recovery time and improve overall outcomes.
Take control of your bone health and recovery journey with our advanced PEMF mat. Experience the transformative effects of PEMF therapy and get back on your feet faster and stronger.
RECOMMENDED PROGRAMS
If you already own one of our PEMF Mats we recommend these programs for Bone Fractures:
-
SEDONA PRO/PRO PLUS PEMF MAT
Sport: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10
-
SEDONA ELITE PEMF MAT
Wellness: 2, 3, 4
Longevity: 1
STUDIES
-
Read Study
PubMed - Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Stimulation of Bone Healing and Joint Preservation: Cellular Mechanisms of Skeletal Response
-
Read Study
PubMed - Pulsed Electro-Magnetic Field (PEMF) Effect on Bone Healing in Animal Models: A Review of Its Efficacy Related to Different Type of Damage
SEDONA WELLNESS PRODUCTS
-
SEDONA PEMF FACEMASK
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price $390.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
TIMMYZZZ PEMF PILLOW
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price $390.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SEDONA PRO PEMF MAT
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price From $5,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SEDONA PRO PLUS PEMF MAT
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price From $6,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SEDONA ELITE PEMF MAT
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price From $7,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SEDONA PEMF CHAIR
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price From $15,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
STIMAWELL EMS BACK MAT
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price $16,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
LONGEVITY LOUNGER PEMF BED
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price From $21,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per