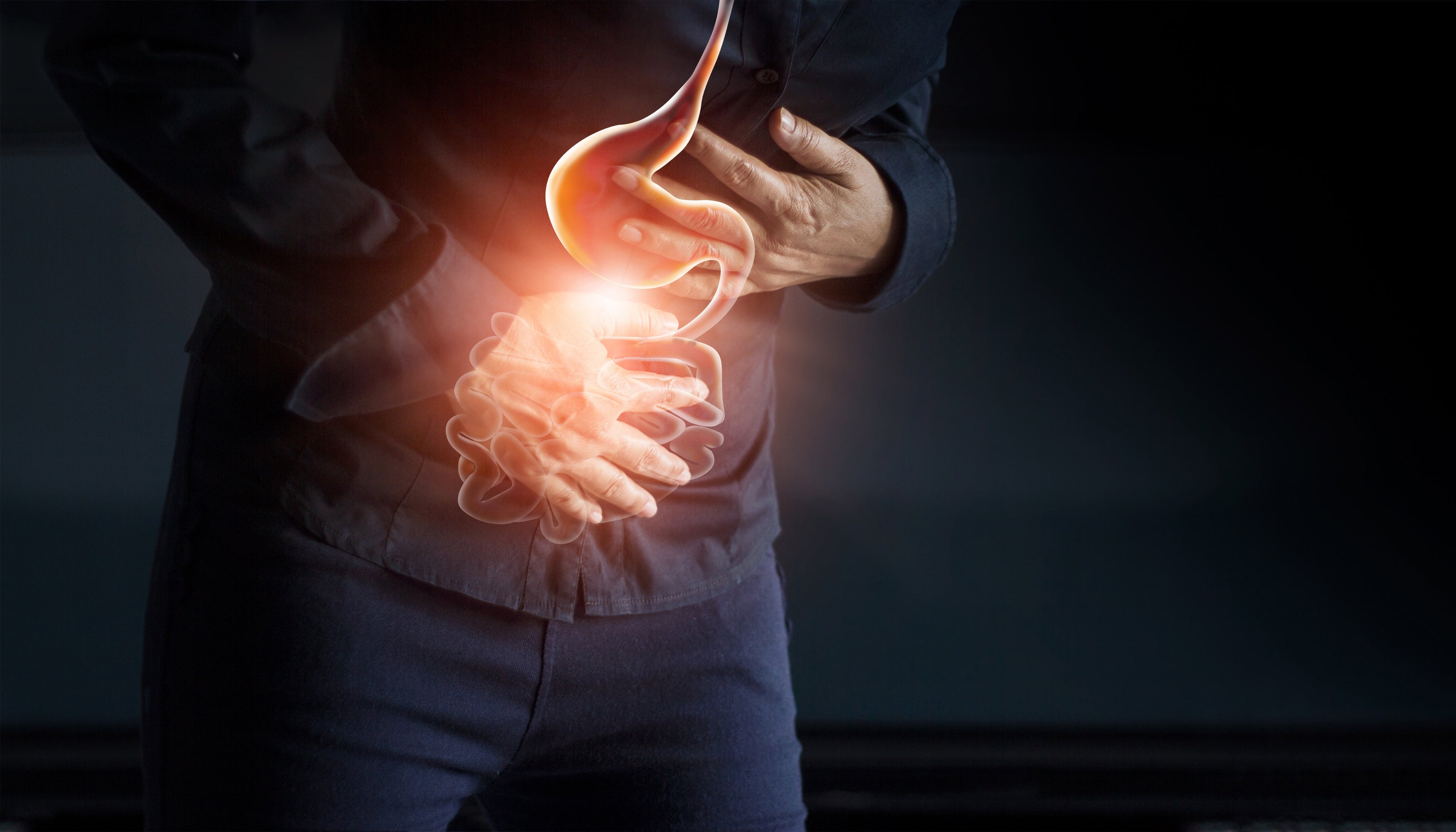
PEMF THERAPY FOR GASTRODUODENITIS
PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy is an innovative treatment approach that can be particularly beneficial for managing conditions like Gastroduodenitis, an inflammation of the stomach and the beginning of the small intestine. By using a PEMF mat, you can leverage the therapeutic benefits of electromagnetic fields to potentially reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and promote overall gastrointestinal health. Here’s how PEMF therapy can assist in managing Gastroduodenitis and why investing in a PEMF mat could be an essential part of your health regimen.
Understanding Gastroduodenitis and PEMF Therapy
Gastroduodenitis presents symptoms such as stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, and sometimes bloating or gas, often caused by infections, excessive alcohol use, or chronic stress. These symptoms arise from the inflammation of the stomach and duodenal lining, leading to discomfort and digestive issues. While traditional treatments typically include medications to reduce stomach acid and manage pain, PEMF therapy offers a complementary treatment by addressing the condition at a cellular level.
How PEMF Therapy Helps with Gastroduodenitis
Reduction of Inflammation:
PEMF therapy is known for its anti-inflammatory effects, which are critical in treating inflammatory conditions like Gastroduodenitis. By reducing cellular inflammation, PEMF therapy can help soothe the stomach lining, decrease swelling, and alleviate the pain associated with the condition.
Pain Relief:
The electromagnetic fields generated by PEMF mats can also have a direct analgesic effect, which helps in reducing the perception of pain. This can be particularly beneficial for acute episodes of Gastroduodenitis where pain management is a priority.
Enhancement of Tissue Repair:
PEMF therapy promotes the regeneration of cells, which is crucial for the healing of the stomach and duodenal linings after damage caused by inflammation. Faster tissue repair can lead to quicker recovery times and help restore the normal function of the digestive system.
Stimulation of Blood Circulation:
Improved blood flow is another significant benefit of PEMF therapy. Enhancing circulation in the abdominal region helps in delivering more nutrients and oxygen to damaged tissues, which supports the healing process and improves overall gastrointestinal health.
PEMF MAT BENEFITS FOR GASTRODUODENITIS
Our PEMF mat is designed with cutting-edge technology to maximize the therapeutic effects for gastrointestinal issues like Gastroduodenitis:
Targeted Treatment:
The mat's broad yet targeted approach ensures that it can effectively cover the gastrointestinal area, providing direct treatment to the parts most affected by Gastroduodenitis.
Customizable Settings:
With adjustable intensity levels and frequency settings, our PEMF mat can be tailored to your specific needs, making it a versatile tool for both acute symptom management and long-term health maintenance.
Ease of Use:
Designed for convenience, our PEMF mat is easy to use at home, allowing for regular sessions that integrate seamlessly into your daily life without the need for continuous medical appointments.
Comfort and Safety:
Constructed from durable, high-quality materials, our mat is safe and comfortable for regular use, ensuring a positive treatment experience.
CONCLUSION
Integrating a PEMF mat into your treatment strategy for Gastroduodenitis can provide significant benefits by reducing inflammation, alleviating pain, enhancing tissue repair, and improving circulation. This therapy offers a non-invasive, drug-free method of treatment that can greatly enhance your quality of life and support your digestive health.
Embrace the healing potential of PEMF therapy and consider how our PEMF mat can become a key component of your wellness routine.
RECOMMENDED PROGRAMS
If you already own one of our PEMF Mats we recommend these programs for Gastroduodenitis:
-
SEDONA PRO/PRO PLUS PEMF MAT
Relax: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
-
SEDONA ELITE PEMF MAT
Wellness: 1, 3, 7
Longevity: 8
STUDIES
-
Read Study
PubMed - Magnetic fields modulate metabolism and gut microbiome in correlation with Pgc-1α expression: Follow-up to an in vitro magnetic mitohormetic study
SEDONA WELLNESS PRODUCTS
-
SEDONA PEMF FACEMASK
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price $390.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
TIMMYZZZ PEMF PILLOW
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price $390.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SEDONA PRO PEMF MAT
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price From $5,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SEDONA PRO PLUS PEMF MAT
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price From $6,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SEDONA ELITE PEMF MAT
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price From $7,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SEDONA PEMF CHAIR
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price From $15,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
STIMAWELL EMS BACK MAT
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price $16,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
LONGEVITY LOUNGER PEMF BED
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price From $21,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per