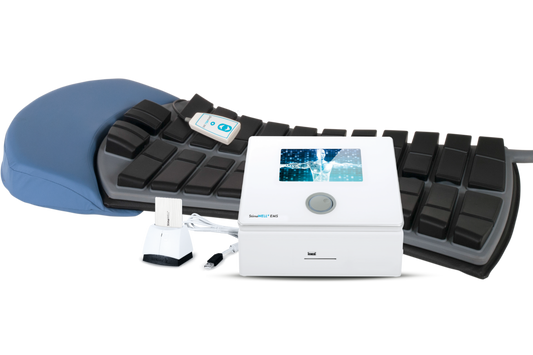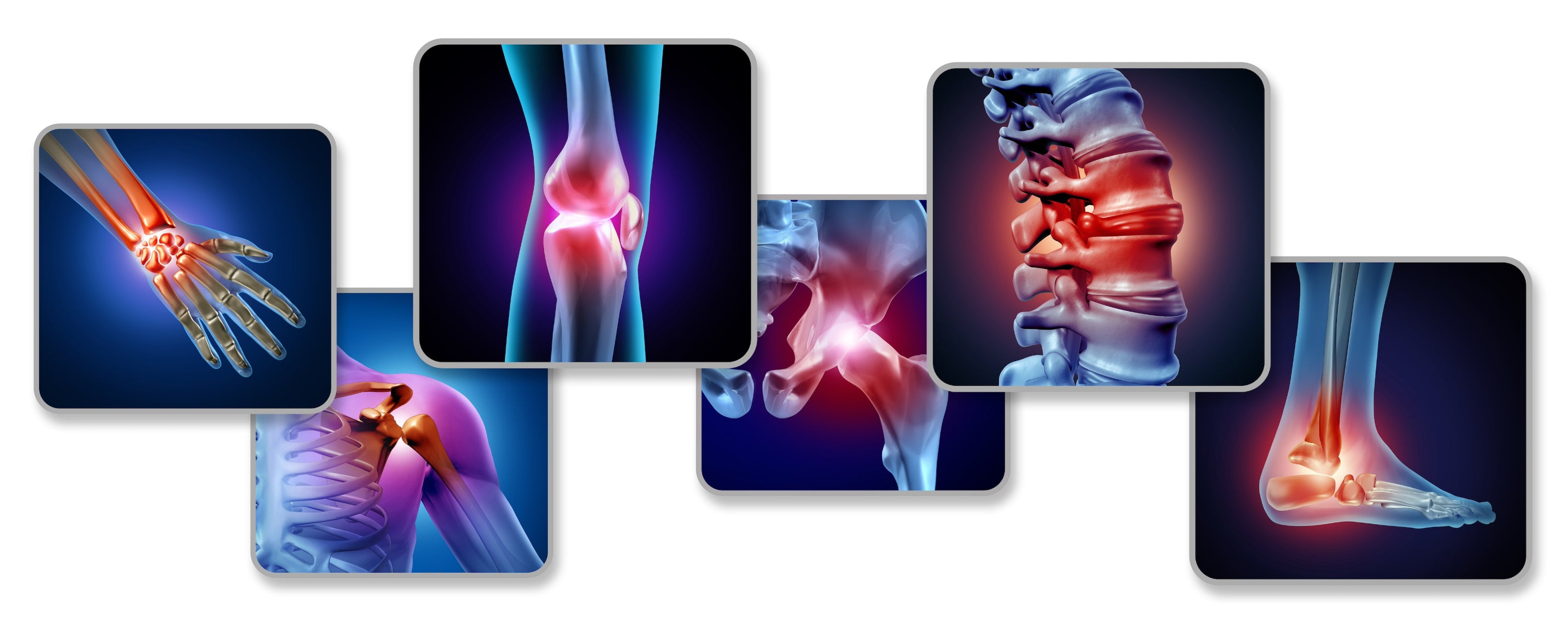
PEMF THERAPY FOR ARTHRITIS
PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy is gaining traction as a non-invasive and effective treatment option for arthritis, a condition characterized by inflammation and degeneration of the joints which causes pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. By using a PEMF mat, individuals suffering from arthritis can potentially see significant improvements in pain management and joint function. Here’s an in-depth look at how PEMF therapy can aid in the management of arthritis and why investing in a PEMF mat could be transformative for your health.
Understanding Arthritis and PEMF Therapy
Arthritis encompasses a range of joint disorders including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and others. These conditions often result in chronic pain and disability. Traditional treatments include medication, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery. PEMF therapy offers an innovative approach by using electromagnetic fields to penetrate the body, enhancing cellular function and tissue repair without invasive procedures.
How PEMF Therapy Helps with Arthritis
Reduction of Inflammation:
Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of many forms of arthritis, particularly rheumatoid arthritis. PEMF therapy helps reduce inflammation by modulating the cellular processes that trigger inflammatory responses. This can result in decreased swelling, redness, and pain, thereby enhancing joint function and comfort.
Pain Relief:
PEMF therapy has proven effective in pain management for arthritis sufferers. The therapy works by influencing the electrical charges of the cell membranes, potentially reducing the transmission of pain signals. This can provide relief from the chronic discomfort associated with arthritis without the side effects associated with some pain medications.
Enhancement of Cartilage Repair:
For conditions like osteoarthritis, where cartilage within the joints deteriorates, PEMF therapy can stimulate the repair and regeneration of cartilage. This is facilitated by the promotion of chondrocyte proliferation, the cells responsible for cartilage repair.
Improvement in Circulation:
Improved blood flow ensures that nutrients and oxygen are delivered to damaged joints, which is crucial for healing and repair. PEMF therapy enhances microcirculation, which supports the overall health of the joint tissues.
PEMF MAT BENEFITS FOR ARTHRITIS
Our PEMF mat is designed to provide optimal therapeutic effects for individuals suffering from arthritis:
Comprehensive Coverage:
The mat's extensive coverage area ensures that all affected joints, whether in the hands, knees, hips, or spine, receive therapeutic electromagnetic fields.
Customizable Settings:
Arthritis affects everyone differently. Our PEMF mat features adjustable settings for intensity and frequency, allowing you to customize your treatment to your specific condition and comfort level.
Ease of Use:
Designed for daily use at home, our PEMF mat is simple to operate, allowing for regular therapy sessions that fit seamlessly into your lifestyle without the need for constant clinical visits.
Safety and Comfort:
Constructed from high-quality materials, our mat ensures safety and comfort during use, making it suitable for prolonged sessions, especially important for those with mobility issues.
CONCLUSION
Adding a PEMF mat to your arthritis management plan offers a unique opportunity to enhance your quality of life. By reducing inflammation, alleviating pain, stimulating tissue repair, and improving circulation, PEMF therapy can significantly reduce arthritis symptoms and potentially decrease dependency on medications.
RECOMMENDED PROGRAMS
If you already own one of our PEMF Mats we recommend these programs for Arthritis:
-
SEDONA PRO/PRO PLUS PEMF MAT
Sport: 5, 8, 9, 10, 11
-
SEDONA ELITE PEMF MAT
Wellness: 4
Longevity: 1, 3, 4, 7, 8
STUDIES
-
Read Study
NIH - Pulsed electromagnetic field therapy for management of osteoarthritis-related pain, stiffness and physical function: clinical experience in the elderly
-
Read Study
PubMed - The Efficacy of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields on Pain, Stiffness, and Physical Function in Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
-
Read Study
Science Direct - Effects of electromagnetic fields on Osteoarthritis
-
Read Study
Oarsi Journal - Treatment of knee osteoarthritis with pulsed electromagnetic fields: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
SEDONA WELLNESS PRODUCTS
-
SEDONA PEMF FACEMASK
Vendor:Sedona Wellness4.75 / 5.0
(4) 4 total reviews
Regular price $390.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
TIMMYZZZ PEMF PILLOW
Vendor:Sedona Wellness4.67 / 5.0
(3) 3 total reviews
Regular price $390.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SEDONA PRO PEMF MAT
Vendor:Sedona Wellness5.0 / 5.0
(12) 12 total reviews
Regular price From $5,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SEDONA PRO PLUS PEMF MAT
Vendor:Sedona Wellness5.0 / 5.0
(8) 8 total reviews
Regular price From $6,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SEDONA ELITE PEMF MAT
Vendor:Sedona Wellness5.0 / 5.0
(20) 20 total reviews
Regular price From $7,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SEDONA PEMF CHAIR
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price From $16,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
STIMAWELL EMS BACK MAT
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price $16,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
LONGEVITY LOUNGER PEMF BED
Vendor:Sedona WellnessRegular price From $21,900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per